Asset Turnover: Formula, Calculation, and Interpretation

She has years of experience in SEO-optimized content creation and focuses on personal finance, investing and banking.
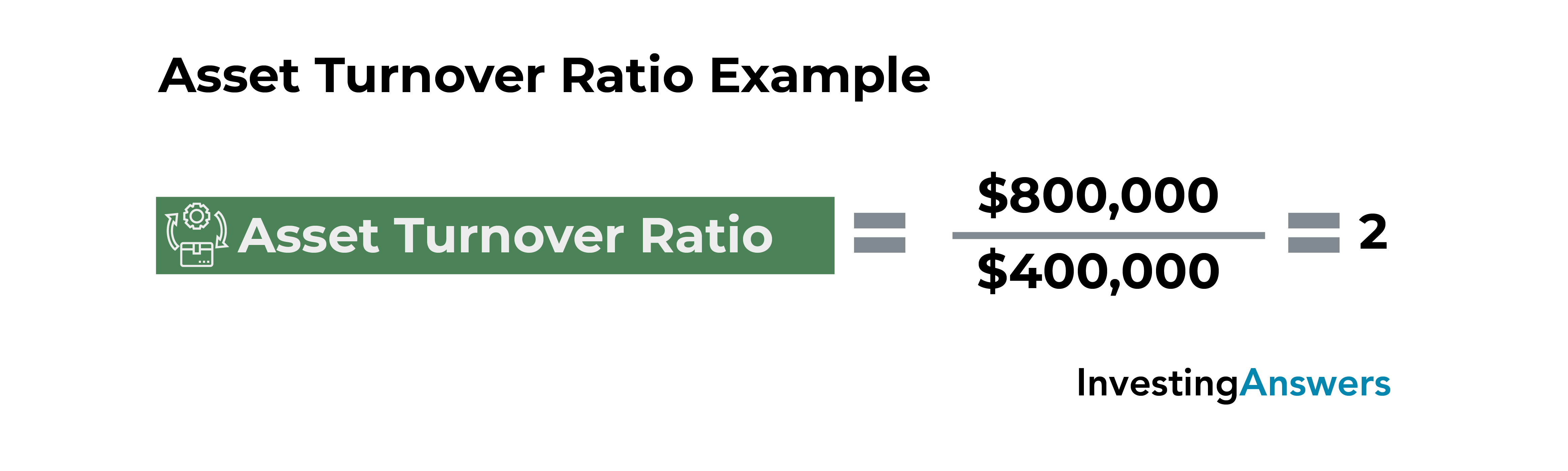
Asset Turnover Calculation (Formula)
Thus, a sustainable balance must be struck between being efficient while also spending enough to be at the forefront of any new industry shifts. GOBankingRates’ editorial team is committed to bringing you unbiased reviews and information. We use data-driven methodologies to evaluate financial products and services – our reviews and ratings are not influenced by advertisers. You can read more about our editorial guidelines and our products and services review methodology. F1[b], F1[e] – Statement of financial position (at the [b]eginning and at the [e]nd of the analizing period). Companies should strive to maximize the benefits received from their assets on hand, which tends to coincide with the objective of minimizing any operating waste.
Low vs. High Asset Turnover Ratios
- A technology company like Meta has a significantly smaller fixed asset base than a manufacturing giant like Caterpillar.
- The asset turnover ratio uses total assets instead of focusing only on fixed assets.
- As with all financial ratios, a closer look is necessary to understand the company-specific factors that can impact the ratio.
- The asset turnover ratio is used to evaluate how efficiently a company is using its assets to drive sales.
- The standard asset turnover ratio considers all asset classes including current assets, long-term assets, and other assets.
- In highly competitive markets, companies might be pressured to streamline operations and optimize asset usage to maintain profitability, potentially leading to higher ratios.
The first step of DuPont analysis breaks down return on equity (ROE) into three components, including asset turnover, profit margin, and financial leverage. Conversely, if a company has a low asset turnover ratio, it means it is not efficiently using its assets to create revenue. As we can see from the calculation done, Walmart and Target both had an asset turnover ratio that is greater than one. Walmart and Target have a high asset turnover ratio because they are both in the retail industry.
Most WantedFinancial Terms
The asset turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that measures a company’s ability to generate sales from its assets by comparing net sales with average total assets. In other words, this ratio shows irs tax forms tax tips and videos how efficiently a company can use its assets to generate sales. The fixed asset turnover ratio is useful in determining whether a company uses its fixed assets to drive net sales efficiently.
She enjoys writing in these fields to educate and share her wealth of knowledge and experience. Transitioning from what this ratio represents, we delve deeper into its application, interpretation, and the caution required when comparing across diverse industry landscapes. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
No, although high fixed asset turnover means that the company utilizes its fixed assets effectively, it does not guarantee that it is profitable. A company can still have high costs that will make it unprofitable even when its operations are efficient. This interplay between asset turnover and profit margins underscores the importance of looking at financial ratios in conjunction.
Your asset turnover ratio will help you—and your business accountant— understand whether or not your business is running efficiently and, subsequently, whether you’re setting it up for success. So, what makes a good asset turnover ratio for your business isn’t necessarily the same as your neighbor’s. In fact, every industry has its own benchmarks, and you’ll want to check yours to see if you’re getting the most out of your assets. We’ll show you how to calculate the asset turnover ratio equation, and why it’s important to understand this accounting term. A firm that outsources manufacturing may have a higher asset turnover due to lower asset base, while a company that invests heavily in its own production facilities may have a lower ratio.
When evaluating the asset turnover ratio, it’s imperative to recognize that industry characteristics can lead to significant variations in what constitutes a ‘healthy’ ratio. Industries that are capital intensive, such as utilities or telecommunications, typically have lower asset turnover ratios due to the high investment in infrastructure required to operate. A company may have record sales and efficiently use fixed assets but have high levels of variable, administrative, or other expenses.
For Year 1, we’ll divide Year 1 sales ($300m) by the average between the Year 0 and Year 1 PP&E balances ($85m and $90m), which comes out to a ratio of 3.4x. The turnover metric falls short, however, in being distorted by significant one-time capital expenditures (Capex) and asset sales. One critical consideration when evaluating the ratio is how capital-intensive the industry that the company operates in is (i.e., asset-heavy or asset-lite). On the flip side, a turnover ratio far exceeding the industry norm could be an indication that the company should be spending more and might be falling behind in terms of development. To stay on top of profitability, they will assess ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, incentivize employees and optimize operations to maximize the bottom line. GOBankingRates works with many financial advertisers to showcase their products and services to our audiences.
